Apriori Algorithm
Apriori Algorithm Overview
Section titled “Apriori Algorithm Overview”The Apriori algorithm is one of the most well-known algorithms for association rule mining and frequent itemset discovery.
Key Concepts
Section titled “Key Concepts”- Frequent Itemset: A set of items that appears together in transactions above a minimum support threshold
- Support: The frequency of occurrence of an itemset in the database
- Confidence: The probability that a rule is correct
Algorithm Steps
Section titled “Algorithm Steps”- Generate 1-itemsets: Find all frequent 1-itemsets (single items)
- Generate k-itemsets: For k ≥ 2, generate candidate k-itemsets from frequent (k-1)-itemsets
- Prune candidates: Remove candidates that have infrequent subsets (Apriori property)
- Count support: Scan database to count support for remaining candidates
- Filter frequent: Keep only itemsets meeting minimum support threshold
- Repeat: Continue until no more frequent itemsets can be generated
The Apriori Property
Section titled “The Apriori Property”Any subset of a frequent itemset must also be frequent.
This property allows us to prune candidate itemsets efficiently.
Pseudocode
Section titled “Pseudocode”L₁ = {frequent 1-itemsets}for (k = 2; L_{k-1} ≠ ∅; k++) { C_k = generate_candidates(L_{k-1}) for each transaction t in database { C_t = subset(C_k, t) for each candidate c in C_t { c.count++ } } L_k = {c ∈ C_k | c.count ≥ min_support}}return ∪_k L_kComplexity
Section titled “Complexity”- Time Complexity: O(2^n) in worst case, where n is the number of items
- Space Complexity: O(2^n) for storing all candidate itemsets
Limitations
Section titled “Limitations”- Multiple database scans required
- Large number of candidate itemsets generated
- Memory-intensive for large datasets
- Performance degrades with increasing number of items
Experimental Results
Section titled “Experimental Results”Our implementation includes comprehensive runtime tracking and visualization. See the Results page for detailed performance analysis and comparison with FP-Growth.
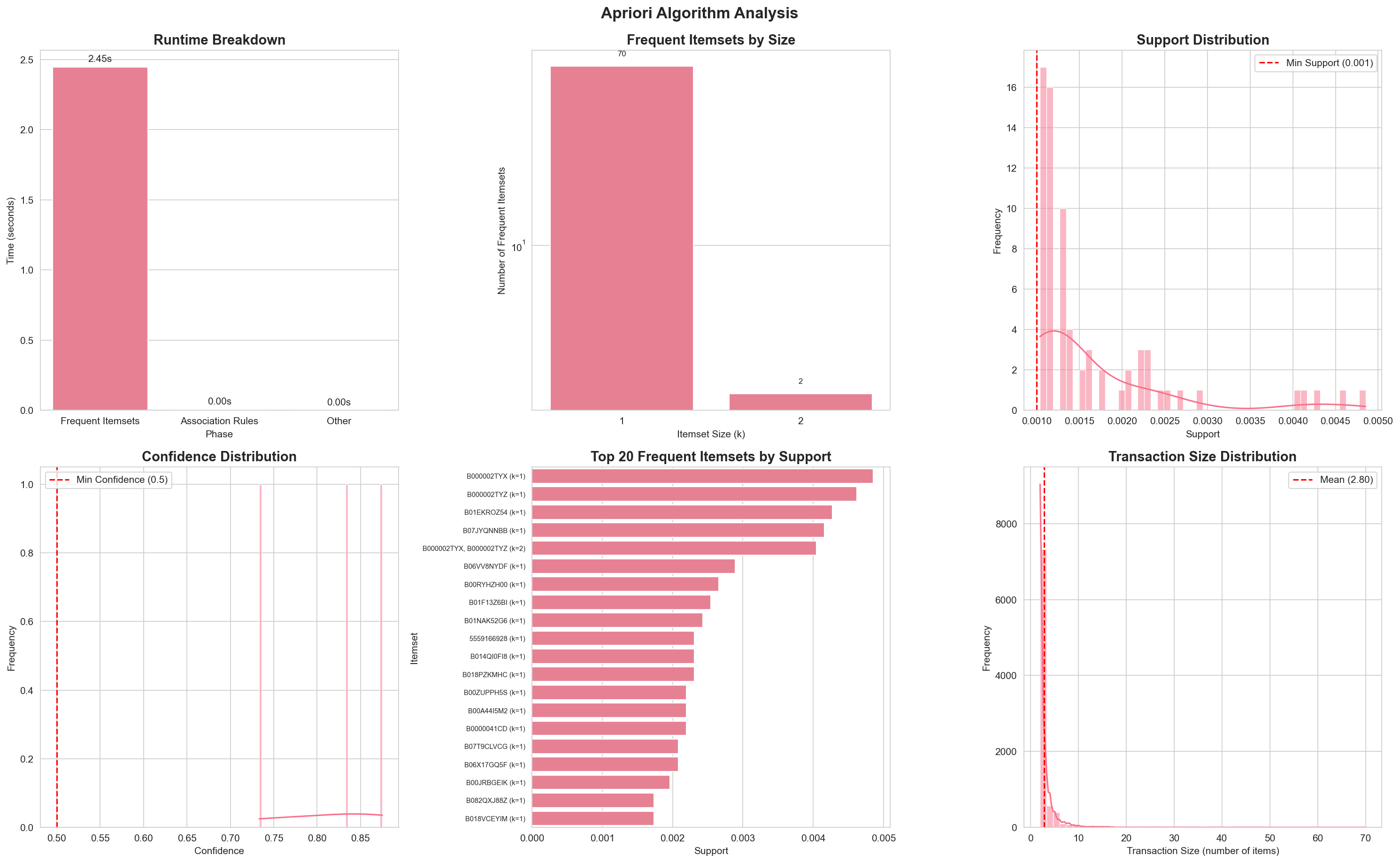
Complete analysis visualization showing runtime breakdown, frequent itemsets by size, support and confidence distributions, top itemsets, and transaction size distribution.
Related Algorithms
Section titled “Related Algorithms”The FP-Growth algorithm addresses many of Apriori’s limitations by using a tree-based approach that avoids candidate generation. See the FP-Growth Algorithm page for details on this alternative approach.